
|
Actinidin is known to
affect the taste,
allergenic properties and characteristics for food processing of the
kiwifruit.
The actinidin concentration and the protease activity in the fruit
juice
were determined in kiwifruit of 13 cultivars obtained in Japan (six Actinidia
deliciosa, five A. chinensis and two A. arguta
cultivars)
by quantitative sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis
and spectrophotometric assay using L-pyroglutamyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-leucine p-nitroanilide
as a substrate. In Abbott,
Koryoku, Kuimi
and Sinzan, both actinidin
concentration
and protease activity in the juice were significantly higher
than those of Hayward, the most common cultivar of
kiwifruit.
In contrast to these cultivars, protease activities in Rainbow
red, Hort16A and Kosui
fruit juice were less than 7% of
that
of Hayward. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Kobayashi39 |
2.6 |
6.7 |
| Pure country |
2.2 |
7.7 |
| First emperor |
1.1 |
4.0 |
| Tear drop |
1.0 |
2.9 |
| Kosen |
N.D. |
0.08 |
| Grape kiwi |
1.8 |
6.5 |
| Sanuki gold |
6.1 |
15.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Hirano |
10.7 |
166 |
| Gassan |
10.6 |
115 |
| Issai |
1.6 |
25.7 |
| Mitsuko |
9.3 |
114 |
| Wild type |
1.7 |
75.1 |
| Baby kiwi (Ananasnaya) |
5.4 |
113 |
| Awaji |
|
0.84 |
| Nagano |
|
0.82 |
| Values represent means of 8-16 experiments. * Synonymous with "Apple kiwi" or "Kaimitsu." **Known commercially as "ZESPRI Gold" kiwifruit. Figures in red: Significantly higher than the corresponding value of Hayward. Figures in blue: Significantly lower than the corresponding value of Hayward. N.D.: not detected |
| Actinidin concentration in the fruit juice was
determined by quantitative SDS-PAGE using purified actinidin as a
standard. Protease activity in the fruit juice was determined by spectrophotometric assay using L-pyroglutamyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-leucine p-nitroanilide as a substrate. |
|
|
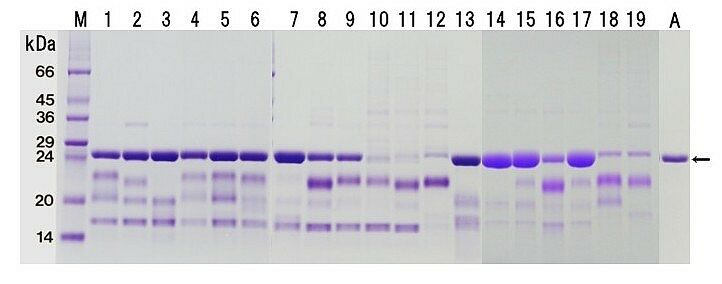
|
| M: Molecular weight marker proteins, 1:
Hayward,
2: Bruno, 3: Abbott, 4: Elmwood, 5: Koryoku,
6: Sanryoku, 7: Kuimi,
8: Koshin, 9: Golden king, 10: Rainbow red, 11:
Hort16A, 12: Kosui,
13: Sinzan, 14: Hirano, 15: Gassan, 16: Issai,
17: Mitsuko, 18: Awaji,
19: Nagano, A: Purified actinidin |